In modern society, touchscreens are utilized across a wide range of applications, from portable smart electronic devices to laptops, tablets, TVs, home appliances, and automobiles, with steadily increasing demand. As a display component, touchscreens require high transparency, or specifically low transmission loss, as an essential optical characteristic to enhance visibility. Optical adhesives are used in touchscreen manufacturing, and the closer the refractive index of the adhesive matches that of the touchscreen panel, the higher the optical transmittance. Therefore, it is crucial to accurately measure the refractive index of the adhesive layer, as it directly influences the visibility of the display. Additionally, since the adhesive is applied in a liquid state and undergoes curing to become solid, which can cause potential changes in refractive index, it is necessary to measure the refractive index of the adhesive layer in its bonded state using a non-destructive, non-contact method.
This study proposes a method for measuring the refractive index and thickness of the internal adhesive layer in touchscreens based on spectroscopic reflectometry in a non-destructive and non-contact manner. For this purpose, a theoretical reflectance model was designed to represent the structure of a three-layer specimen, in which the adhesive layer is interposed between two glass substrates. Both the refractive index and thickness of the adhesive layer were simultaneously determined by fitting the designed reflectance to the measured one [1]. Two types of specimens with different adhesives and glass were measured. As shown in Fig. 1, the performance of the proposed method was evaluated by comparing with measurement results by the prism refractometry. This study demonstrates the potential for precisely measuring the refractive index and thickness of adhesive layers in touchscreens in a non-destructive and non-contact manner, thereby contributing to the enhancement of display visibility and quality control.
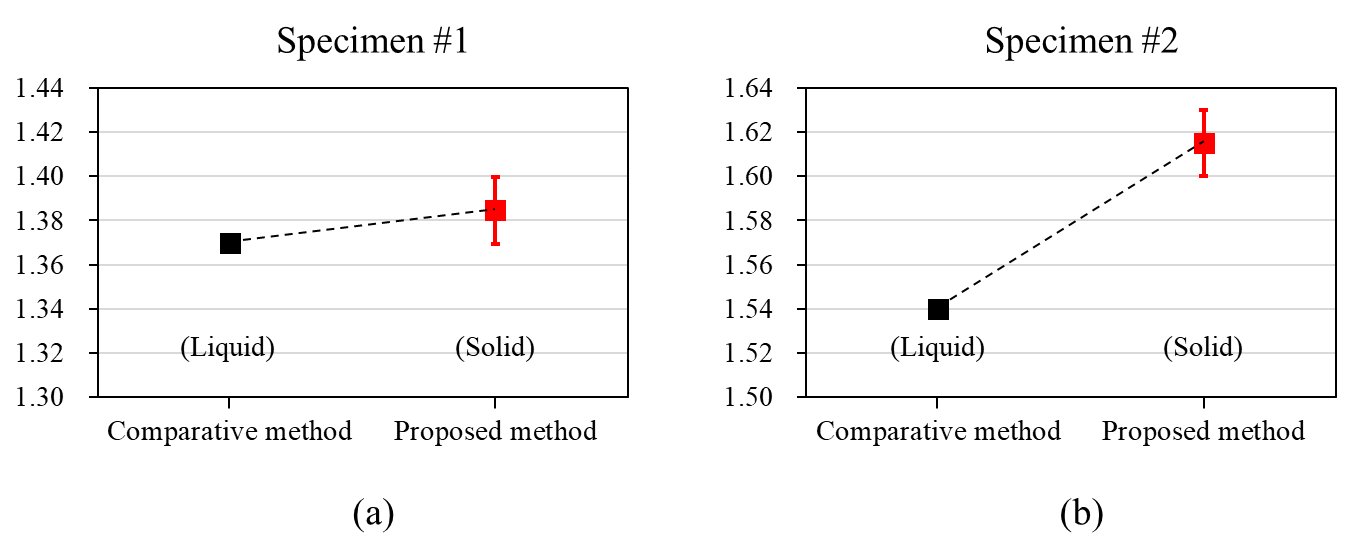
Fig. 1. Refractive index measurement results of the proposed method and a comparative method for (a) Specimen #1 and (b) Specimen #2